Drawing Orienteering Maps in OCAD
The focus of this tutorial is how to draw an orienteering map with OCAD. It doesn’t matter if you start a new mapping project or update an old existing map. It is a complement to the PDF Getting Started with OCAD, which you can download from the Help Menu in the OCAD software.
About OCAD
Run OCAD
OCAD 2018 Orienteering and OCAD 2018 Mapping Solution are new available as 64-bit version and 32-bit version. The OCAD Setup installs both versions.
For normal use, the 32-bit version is sufficient. Please note, the 64-bit version isn't faster than the 32-bit version. The big advantage of 64-bit is that OCAD can allocate more than 3 GB RAM if available on the computer. That is important when loading huge raster background maps or DEM files.
Structure of the OCAD User Interface
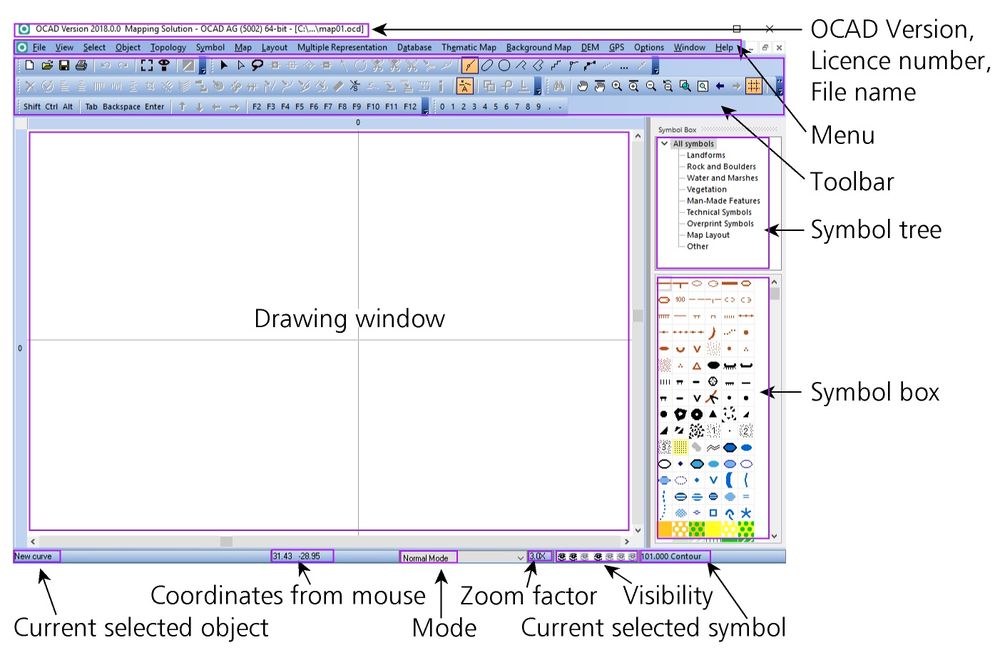
The image below shows you the OCAD User Interface.
OCAD Help
You will find the following submenus in the Help menu.
- Contents: Opens the OCAD Main Page.
- Menu: Help for menu commands.
- Toolbar: Help for toolbar buttons.
- Tutorial: Link to the OCAD Tutorials.
- What is New: See the newly added functions on this page.
- OCAD Home page: Opens OCAD homepage on the Internet.
- OCAD Service Update: Download the current Service Update.
- OCAD Tutorial Videos: Connect to Learning Videos on OCAD homepage.
- OCAD Youtube Channel: OCAD Youtube Channel
- Getting Started with OCAD 2018: Open the PDF file 'Getting Started with OCAD 2018'. For different languages see here
- OCAD Blog: Show the newest posts from the OCAD Blog.
- License Transfer Utility: Opens the License Transfer Utility to deactivate your license and transfer it to another user.
- License Manager: The License Manager tool shows an overview about the OCAD licenses which are assigned to your organization (company or association).
- About OCAD: General Information about OCAD like license information and current version of OCAD.
Service Update
Regular and free updates are included in the OCAD subscription model. The Service Update corrects known bugs and adds the latest cartography tools and enhancements to your OCAD.
Therefore we recommend using OCAD software always with the most recent Service Update to benefit from the quality improvements.
Please download the current Service Update from the Help -> OCAD Service Update function in the OCAD program.
The content of the Service Update is listed in the Release notes. Your current version of OCAD can be seen under About OCAD in the Help menu.
New Map
Start a New Map File
Before start mapping you should define which type of map you want to draw, which symbol set you want to use and which scale the map should have. For this tutorial we want to draw an normal forest orienteering map in scale 1:10'000.
To create a new map:
- Select New in the File menu. The New File dialog box appears.
- Choose a map type. OCAD provides predefined symbol sets to help you begin drawing your map immediately. Choose the symbol set Orienteering Map ISOM 2017 10000.ocd.
- Deside in which scale the map shall be drawn. Set the scale to 1:10'000.
- Choose the language of the symbol set. (only at ISOM 2017 available)
- By clicking the OK button, OCAD creates a new map and copies the chosen symbol set to it.
Click here to learn more about this step.
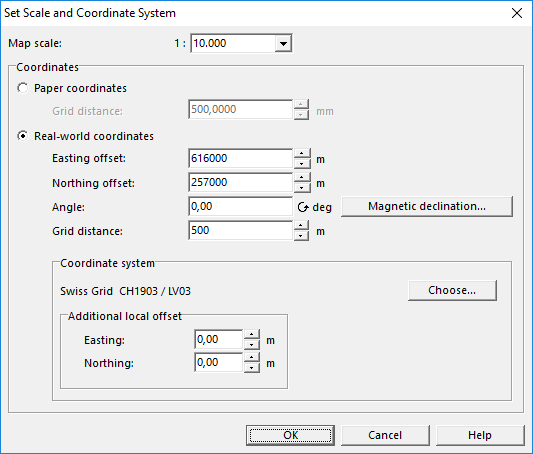
Set Scale and Coordinate System
Select the Set Scale and Coordinate System item from the Map menu. The Set Scale and Coordinate System dialog box appears.
Enter the Map Scale
Enter a scale and click the OK button.
![]() Do not use this dialog to change the scale after entering the initial values. To increase or decrease the size of the map subsequently, use the Change Scale function in the Map menu. Setting the current scale does not enlarge or reduce the map. It only changes a number in the map file and georeferencing will be lost.
Do not use this dialog to change the scale after entering the initial values. To increase or decrease the size of the map subsequently, use the Change Scale function in the Map menu. Setting the current scale does not enlarge or reduce the map. It only changes a number in the map file and georeferencing will be lost.
Georeference the Map
Before loading a georeferenced Background Map, work with GPS data or import Spatial Base Data, we recommend that you first georeference the map. Georeferencing means, that you assign space-related reference information to objects in a spatial reference system. Shortly: A georeferenced map is assigned to a coordinate system. You should contact your data supplier, national surveying office or cartographic institute to find out which coordinate system will best suit your needs.
- Choose wheter you want define Paper coordinates (in mm) or Real world coordinates. We choose Real world coordinates for this tutorial.
- In the Easting offset and Northing offset fields, enter the coordinate values for the center of your map.
- The coordinate system can be rotated by entering a value in the Angle field. The "Angle" is the deviation from the magnetic North to the coordinate system. At the moment there are 0-degree deviation in Switzerland.
- In the Grid distance field, enter the desired distance for the Coordinate Grid lines.
![]() Enter the coordinate values for the center of your map in the horizontal and vertical offset fields. This is important since the drawing area of OCAD is limited to 4 x 4 m in the
Enter the coordinate values for the center of your map in the horizontal and vertical offset fields. This is important since the drawing area of OCAD is limited to 4 x 4 m in the Orienteering edition, in the
Starter edition as well as in the
Course Setting edition and 80 x 80 m in the
OCAD Mapping Solution. This option is used to ensure that imported Spatial Base Data, georeferenced Background Maps and GPS measurements do not lie outside the drawing area.
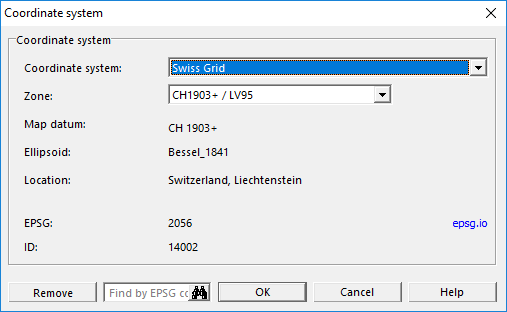
Coordinate System
Click the Choose button to define a coordinate system. The Coordinate System dialog appears.
Choose the desired coordinate system. OCAD supports a lot of coordinate systems.
Click here to learn more about Scale, Coordinat System and Georeferencing.
Create the Base Map for the Field Work
Before you go mapping into the terrain, you should try to create the best possible base map. The more you invest in your base map, the faster and more accurate your mapping will be. In OCAD you can import spatial data, old orienteering maps, derive own base maps with LiDAR data and combine them.
Raster Base Maps
Typically, the orthophotos and topographic maps for orienteering maps are delivered as raster files. OCAD 2018 supports, among others, the most common used raster files: JPG, TIFF and PNG.
Orthophotos and topographic maps are mostly georeferenced. Raster files are georeferenced, when the pixels are referenced with the coordinates. Normally the georeferencing data is saved in a world file. The world file has the same file name as the raster file, but with another file extension: JPG → JGW, TIFF → TFW, PNG → PGW.
Open Georeferenced Raster Base Map as Background Map
Click to Background Map->Open
If there's not yet a coordinate system and offset, the Background Map (Georeferenced) dialog appears and shows the georeferencing of the selected background map.
Click OK.
Open not Georeferenced Raster Base Map as a Background Map
Click to Background Map->Open
It the seleced file is not georeferenced, you need to enter a resolution for the background map (if a raster map is loaded) and click the OK button.
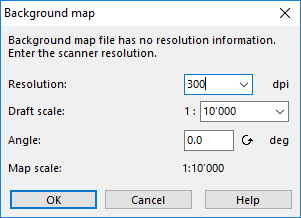
The background map is displayed at the center of the current drawing area. The raster map (background map) now needs to be adjusted with the map (Adjust a Background Map). In other words, it needs to be referenced with the map coordinate system.

File:Hilt.jpfWe recommend you to print the grid on the base map. Thereby you can adjust your scanned base map easier. In the dialog File->Print select Print screen grid and choose the Grid color.
Preparation of LiDAR Data
LiDAR data is often a base for orienteering maps and highly recommended to use if available. LiDAR data is available as a point cloud in the las/laz file format. With LiDAR data, you can easily get lot of information about the terrain and the vegetation, which will make mapping much faster and more accurate.
For this purpose, there's an extra tutorial about Using_Airborne_Laserscanning_Data_for_Orienteering_Base_Map_Generation There you will learn, how to proceed LiDAR data in OCAD and how to use them when drawing orienteering maps..
Import Vector Data
Vector data can also be used to create the base map. The advantage is that vector data contain point, line, area and text objects which are directly converted to map objects during the import into OCAD. It saves a lot of time because especially in urban surroundings many map objects can be created automatically instead of being digitized manually. Governmental data is generally available as DXF or Shape files. OCAD can also import other vector data formats like PDF, AI, SVG or OSM (Open Street Map).
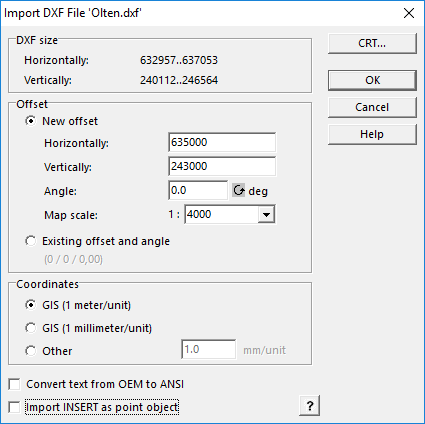
- Go to File->Import
- Choose an importable file, e.g. a dxf-file.
- The vector data is shown as Unsymbolized objects in the drawing area. You can symbolize the objects automatically:
- The map now shows all objects with the assigned symbols.
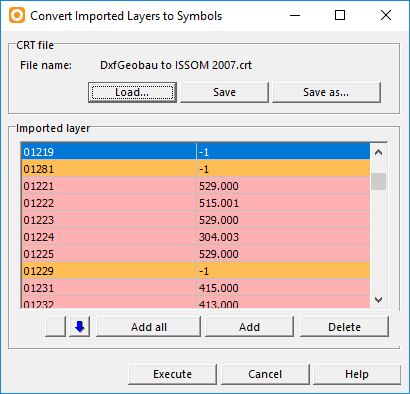
![]() You can also Convert the imported Layers manually.
You can also Convert the imported Layers manually.