Import Files: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(/* Import OCAD Map File:Space.PNGThis function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartographyThis function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteeringThis...) |
||
| (161 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Choose this command to import an external file to the current map. The '''Import''' dialog box is displayed. Initially all importable files are listed. The following file types can be imported: | Choose this command in the '''File''' menu to import an external file to the current map. The '''Import''' dialog box is displayed. Initially all importable files are listed. The following file types can be imported: | ||
* OCAD map files (*.ocd) | * OCAD map files (*.ocd) | ||
* Adobe Illustrator files (*.ai) (only vector data) | * Adobe Illustrator files (*.ai) (only vector data) | ||
* CSV files (*.csv) | |||
* DXF files (*.dxf) | * DXF files (*.dxf) | ||
* Enhanced Meta files (*.emf) (only vector data) | * Enhanced Meta files (*.emf) (only vector data) | ||
* GML files (*.gml) | |||
* GPX files (*.gpx) | * GPX files (*.gpx) | ||
* KML files (*.kml) | |||
* OpenStreetMap files (*.osm) | * OpenStreetMap files (*.osm) | ||
* | * NMEA files (*.nmea) | ||
* PDF files (*.pdf) (only vector data) | * PDF files (*.pdf) (only vector data) | ||
* Freehand XML files (*.rcw) | * Freehand XML files (*.rcw) | ||
| Line 15: | Line 18: | ||
* xyz files (*.xyz) | * xyz files (*.xyz) | ||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] It is possible to select and import multiple dxf, gpx, nmea, shp and xyz files in this dialog box. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] OCAD opens the File Dialog in the folder of the last imported file. Press the '''Shift''' key to open a file from the ''Templates'' folder. The ''Templates'' folder is a subfolder of OCAD program folder (e.g. ''C:\Program Files\OCAD\OCAD 12 Mapping Solution\Templates''). | |||
==Import OCAD Map [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]][[File:Sta40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Starter.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
==Import OCAD Map== | Choose an OCAD-File (*.ocd) in the '''Import''' dialog box and click the open button. The '''Import OCAD Map''' dialog appears with the following options: | ||
'''Position''' | '''Position''' | ||
* '''Place using the mouse:''' Choose this option to import a logo. The imported map is displayed in the center of the screen and you can drag it with the mouse to the desired position. | * '''Place using the mouse:''' Choose this option to import for example a logo. The imported map is displayed in the center of the screen and all objects are selected. Thus, you can drag it with the mouse to the desired position. | ||
* '''Place with offset:''' Choose this option when combining different parts of a map. Enter the offset in mm where the origin (0, 0) of the imported map should be placed. | |||
* '''Use real world coordinates:''' Choose this option to import a georeferenced map. The map is automatically placed at the correct position. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] There will be a warning if the coordinate systems are different. | |||
: | |||
'''Symbols''' | |||
* '''Do not import any symbols and colors:''' Choose this option to not import any symbols and colors. | |||
* '''Import symbols only if symbol number does not exist yet:''' Choose this option to import symbols only if the symbol number does not exist yet. The symbol signature will not be compared. OCAD will not produce a new symbol if there is a symbol with an equal symbol number but a different signature. Colors will not be imported. | |||
* '''Import symbols that do not exist. If the imported symbol number exists then a new symbol number is applied:''' Choose this option to import symbols if they do not exist. OCAD will produce a new symbol if there is a symbol with an equal number but a different signature. The new symbol number gets the next unused decimal (e.g. 102.001 becomes 102.002). Colors will not be imported. ''This option accords with the data import function of OCAD 8.'' | |||
* '''Import all symbols and colors:''' Choose this option to import all symbols and colors from the imported map(for example to print 2 maps with different symbol sets and color tables). There are two options to import the [[Map#Colors|'''Colors''']] either ''at the top'' or ''at the bottom'' of the color table. | |||
* '''Change symbol status from Normal to Protect:''' Check this option to change to symbol status off the imported symbols from [[Symbol#Normal|Normal]] to [[Symbol#Protect|Protect]]. This option is recommanded for importing an ocd map into a course setting project. | |||
* '''Rotate objects with symbols orientated to north:''' This option is only available if the [[Create_a_New_Map#Set_Scale_and_Coordinate_System|'''Real world coordinates''']] options are turned on in the current and the imported map file and if the real world angle property is different in both maps. Select this option if the imported objects with north oriented symbols shall be rotated by this angle difference. | |||
* '''Use CRT file:''' Activate this button to use a CRT converting table. This table consists of two columns, which are separated by a blank. In the first column there is the symbol number of the OCAD symbol in the map which is to be imported. In the second column there is the symbol number of the opened OCAD file. Visit the '''[[Cross Reference Table]]''' page to get more information about CRT-Files. | |||
: '''Example:''' | : '''Example:''' | ||
: <PRE>526.0 813.1</PRE> | : <PRE>526.0 813.1</PRE> | ||
: That means that all objects with the symbol number 526. | : That means that all objects with the symbol number 526.000 will get the number 813.001 after the import. | ||
* '''Load:''' Click this button to load a CRT file. | * '''Load:''' Click this button to load a CRT file. | ||
'''Database''' | |||
* '''Database, Import existing database connections:''' This option is enabled if the import file contains database connections. When this option is choosen then OCAD creates a new database connection to the existing database if there is not already a database connection with the same name and file path in the OCAD file. Please note that OCAD creates a new connection with a new name if a dataset with the same name but another file path exists. Otherwise OCAD uses the existing dataset. OCAD does not merge databases. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] Please note that this CRT file is not compatible with the CRT files created in | [[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] Please note that this CRT file is not compatible with the CRT files created in | ||
[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbol|Convert Layers]] dialog!<br> | '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbol|Convert Layers]]''' dialog! A list of all CRT-Files which can be used with OCAD can be found on the '''[[Cross Reference Table]]''' page.<br> | ||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] The error message: "Cannot import symbol" appears if OCAD could not import a symbol. The import is aborted. | [[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] The error message: "Cannot import symbol" appears if OCAD could not import a symbol. The import is aborted. | ||
== | ==Import Adobe Illustrator File [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | ||
Choose an Adobe Illustrator file (*.ai) in the '''Import''' dialog and click the open button. Files from Illustrator version 4 and later can be imported.<br> | |||
The objects from an Adobe Illustrator file are imported into OCAD as [[Image_Objects|image objects]]. The layer names are imported with the objects. The layer name is displayed in the left part of the status bar if an image object is selected. <br> | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] Use '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects. | |||
==Import DXF File [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]][[File:Sta40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Starter.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
DXF stands for Drawing Exchange Format and is a CAD data file format developed by Autodesk made for data exchange between AutoCAD and other programs (Read more in the '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dxf Wikipedia Article]'''). | |||
Choose a DXF-File (*.dxf) in the '''Import''' dialog and click the open button. | |||
[[File:DxfImport1.png]] | |||
The '''Import DXF-File''' dialog appears with the following options and information: | |||
* '''DXF size''': This box shows the range of the coordinates in the DXF file. | |||
* '''Offset''': Choose here whether you want to change the OCAD real world coordinates or to keep the existing ones. | |||
** '''New offset:''' Choose this option if no real world coordinates are defined for the map. If you leave the proposed offset unchanged, the imported objects will be placed in the center of the OCAD drawing area. In addition, you can set the desired scale of the OCAD map here. | |||
** '''Existing offset and angle:''' Choose this option if the map already has real world coordinates and you want to fit the imported DXF file to the existing coordinates. | |||
* '''Coordinates:''' Define here how the coordinates of the DXF file should be interpreted. OCAD does not support WGS 84 coordinates. | |||
** '''GIS''' (1 meter/unit): Choose this option when importing DXF files from Geographic Information Systems (GIS), where 1 unit in the DXF-File corresponds to 1 meter in the real world. The map scale is used for the transformation. Choose '''[[Create_a_New_Map#Set_Scale_and_Coordinate_System|Scale and Coordinate System]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu to set the map scale. | |||
* | ** '''GIS''' (1 millimeter/unit): Choose this option when importing DXF files from Geographic Information Systems (GIS), where 1 unit in the DXF-File corresponds to 1 millimeter in the real world. Usually GIS data uses the unit meter. Please check the unit of the dxf data before importing the data into OCAD. | ||
* | This example is from British Ordnance Survey data. The dxf size and the proposed new offset is in millimeter. | ||
[[File:DxfImport2.png]] | |||
** '''Other:''' Choose this option when importing DXF files from graphic programs. Enter the size in millimeters of one DXF unit on the map (e.g. if the DXF units are inches, enter 25.4). | |||
* '''Convert text Objects from OEM to Unicode: ''' Activate this box if the text in the DXF file is encoded in the OEM character set. OEM character set is used by old DOS programs and concerns only accented characters (ä, à, å etc.). Windows programs normally produce text in the ANSI character set. If accented characters are not imported correctly, try this option. | |||
: '''Other:''' Choose this option when importing DXF files from graphic programs. Enter the size in millimeters of one DXF unit on the map | |||
* '''Convert text Objects from OEM to Unicode: ''' Activate this box | |||
If accented characters are not imported correctly, try this option. | |||
* '''Import INSERT as point object:''' Activate this option to import INSERT objects in the DXF file as point objects in OCAD. Otherwise the definition of INSERT objects is imported. | * '''Import INSERT as point object:''' Activate this option to import INSERT objects in the DXF file as point objects in OCAD. Otherwise the definition of INSERT objects is imported. | ||
* '''CRT:''' Click this button if you have converted a similar DXF file before using '''Convert layers'''. A file dialog box appears. Choose the CRT file created with the '''Convert layers''' command. Read more about CRT-Files on the '''[[Cross Reference Table]]''' page. You will find examples there, too. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg]] If you do not use a CRT-File for importing a DXF-File, the DXF objects are imported as '''[[Unsymbolized Objects]]'''. Use the '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' function in the '''[[Map]]''' menu to assign the objects to a symbol later on. | |||
==Import EMF File [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose this function to import Windows Enhanced Metafile. | |||
This is | This import file format is obsolete. | ||
==Import GML Files[[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]] == | |||
Choose | Choose this function to import [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normbasierte_Austauschschnittstelle Normbasierte Austauschschnittstelle (NAS)] data. | ||
OCAD cannot import other GML files. | |||
==Import | ==Import GPX File [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | ||
Choose the .gpx file format in the '''Import File''' dialog. Read more about importing GPX files in the '''[[GPS#Import from File|GPS - Import from File]]''' article. | |||
''' | This function is also available for the [[File:Sta40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Starter.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]] '''OCAD 12 Starter''' and the [[File:CS40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Course Setting.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]] '''OCAD 12 Course Setting''' Edition. For this purpose, choose the '''[[GPS#Import from File|Import from File]]''' command in the '''[[GPS]]''' menu. | ||
''' | ==Import KML File [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]] == | ||
Choose the '''*.kml''' format in the file import dialog to import [https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language Keyhole Markup Language (KML)] files. <br>The line color, line width and fill color of the objects is also imported. | |||
==Import OSM Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]][[File:Sta40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Starter.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
A description of this function with an example can be found on the '''[[Import Open Street Map Files]]''' page. | |||
==Import NMEA Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose the .nmea file format in the '''Import File''' dialog. Read more about importing NMEA files in the '''[[GPS#Import from File|GPS - Import from File]]''' article. | |||
This function is also available for the [[File:Sta40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Starter.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]] '''OCAD 12 Starter''' Edition. For this purpose, choose the '''[[GPS#Import from File|Import from File]]''' command in the '''[[GPS]]''' menu. | |||
==Import PDF Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose a '''PDF-File''' in the '''Import''' dialog and click the '''Open''' button. The '''Save Cross Reference Table''' dialog appears. If you want to save a CRT-File, click the '''Save''' button. If you want to continue without saving a CRT-File, click the '''Cancel''' button. Learn more about CRT-Files on the '''[[Cross Reference Table]]''' page. | |||
The PDF-File is displayed in the middle of the current view of the map. All objects are selected, hence, it can be easily moved to the desired position. | |||
Please note, that it is only possible to import vector PDF-Files. If the PDF-File contains raster images, they are displayed as a grey area on the map. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg]] Vector objects in PDF-Files are imported as '''[[Image Objects]]''' and can be converted to symbols using the '''[[Map#Convert Imported Layers to Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbols]]''' function. Learn how to make a point symbol out of a vector graphic by reading the '''[[Create_a_New_Point_Symbol#Create_a_Point_Symbol_out_of_Vector_Data|Create a Point Symbol out of Vector Data]]''' article. | |||
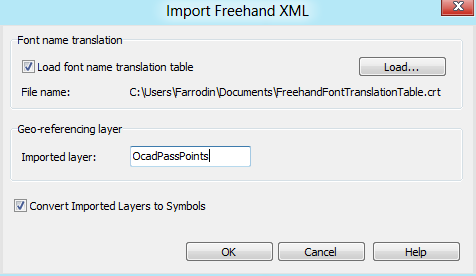
==Import Freehand XML Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]]== | |||
[[File:ImportFreehandXml.PNG]] | |||
Choose a Freehand XML File (*.rcw) in the Import dialog and click the open button. The '''Import Freehand XML''' dialog appears with the following options: | |||
'''Font name translation:''' | |||
* Select the '''load font name translation table''' option if the Macintosh font names used in the Freehand XML file should be translated to the Windows font names. This translation is defined in a cross reference table (*.crt). | |||
: '''Example:''' | |||
: <PRE>NicV-Normal;NicV</PRE> | |||
: That means the font of all objects that used the '''NicV-Normal''' in Freehand will be changed to '''NicV''' after the import. | |||
* '''Load:''' Click this button to load a CRT file. | |||
* '''File name:''' The file name of the loaded CRT file is shown here. | |||
'''Geo-referenceing layer:''' | |||
* '''Imported layer:''' OCAD offers a coarse georeferecing for Freehand XML files if the Freehand XML file contains a layer with coordinate values. This layer must be entered in the '''imported layer''' text box. | |||
'''Convert imported layers to symbols:''' | |||
* Select this option if the imported layers should be converted to OCAD symbols. This step can be done also after the import by using '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu. | |||
==Import Shape Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]]== | |||
Get some information about '''Shape Files''' on '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shape_file Wikipedia]'''. | |||
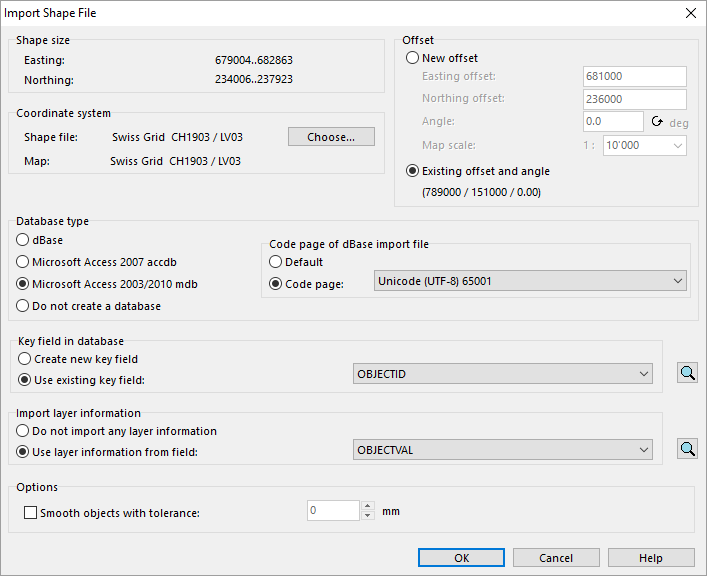
If you choose an '''ESRI Shape File''' in the '''Import''' dialog, the '''Import Shape File''' dialog appears. | |||
[[File:ImportShapeFile.PNG|707px]] | |||
The import dialog offers the following options: | |||
'''Shape size:''' | |||
* This box shows the dimension of the data in the shape file using its coordinates. | |||
'''Coordinate System:''' | |||
* This box allows you to transform the imported Shape file data to the maps coordinate system. Click the '''Choose''' button to choose the Shape file's coordinate system if it is different to the map coordinate system. | |||
'''Offset:''' | '''Offset:''' | ||
* '''New offset:''' Choose this option when importing the first shape file to the actual map. OCAD | * '''New offset:''' Choose this option when importing the first shape file to the actual map and if the map is not georeferenced yet. OCAD proposes reasonable easting and northing offset values. OCAD also proposes a map scale that the entire map in the shape file fits into the drawing area of OCAD. | ||
* '''Existing offset and angle:''' Select this option when importing the second and the following shape file to the actual map. The new shape file will then fit to the already imported shape files. | * '''Existing offset and angle:''' Select this option when importing the second and the following shape file to the actual map or if the map is already georeferenced. The new shape file will then fit to the already imported shape files. | ||
'''Key field in | |||
'''New database type:''' | |||
* When importing Shape files, OCAD creates a new database for each Shape file. You can choose between the database types '''dBase''', '''Microsoft Access 2007 accdb''' and '''Microsoft Access 2003/2010 mdb'''. | |||
* Microsoft Access databases are much faster than dBase and support Unicode. dBase is more compatible with Shape export. | |||
* If one of the Microsoft Access options is chosen then the '''code page''' of the imported Shape file's dBase file should be declared. This is important to ensure a correct text conversion from dBase (Ansi) to Microsoft Access (Unicode) conversion. | |||
* Choose '''Do not create a database''' when you do not need the attribute data. Then OCAD imports only the geometry from the Shape file. You can add one attribute as layer name when choosing the option '''Use layer information from field'''. | |||
'''Key field in database:''' OCAD creates a copy of the Shape file's dBase file during the import process. OCAD can optionally add an additional key field to the copied dBase file. | |||
* '''Create new key field:''' Select this option, if the dBase file does not contain a key field with a unique key for each object or if you are not sure if such a key field exists. | * '''Create new key field:''' Select this option, if the dBase file does not contain a key field with a unique key for each object or if you are not sure if such a key field exists. | ||
* '''Use existing key field:''' Select this option, if the dBase file already contains a key field and you are sure that it contains a unique key for each object. Select the key field. | * '''Use existing key field:''' Select this option, if the dBase file already contains a key field and you are sure that it contains a unique key for each object. Select the key field. | ||
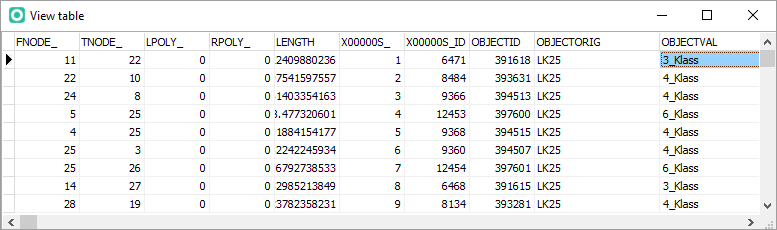
* '''View table:''' Click on this button to see the dBase table. The '''[[Database#View_and_edit_table|View Table]]''' dialog opens. This table helps to decide which key field can be used. It is not possible to edit this table. | |||
''' | '''Import layer information:''' | ||
* '''Do not import any layer information:''' Select this option if no layer information should be imported. Symbols must be assigned with '''[[Database#Assign_Symbols_by_Records|Assign Symbols by Records]]''' command in '''[[Database]]''' menu. This may takes a lot of time. | |||
* '''Use layer information from field:''' Select this option if you want to import layer information (ex. lake, forest etc.) from a specified dBase field. This allows you to choose '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu to assign symbols to the imported data.<br> | |||
* '''View table:''' Click on this button to see the dBase table. The '''[[Database#View_and_edit_table|View Table]]''' dialog opens. This table helps to decide which field contains the layer information. It is not possible to edit this table. | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg]] Check the '''Field 2''' box to choose a 2nd database field. In that case the imported layer information will be both field values, concatenated by an underscore: FieldValue1_FieldValue2. | |||
: [[File:ShapeImportLayerField2.png]] | |||
'''Smooth objects''' | |||
Additional option whether objects imported from shape file should be smoothed with a tolerance. | |||
==Import | ===Import Text or Line Text Objects=== | ||
There are no text objects in Shape files. The texts like city names or river names are stored as attributes of the objects in the Shape file's dBase file. You can create text objects from imported point objects or line text objects from imported line objects by using [[Database#Add_Texts_by_Records|'''Add Texts by Records...''']] in the '''[[Database]]''' menu. | |||
The '' | ====Example==== | ||
After importing the Shape file the objects appear in OCAD as [[Unsymbolized Objects|unsymbolized objects]]. | |||
The label of the selected object is stored in the according database record ('Baar' in the field 'TEXT'). | |||
[[File:ImportShapeText1.png|600px]] | |||
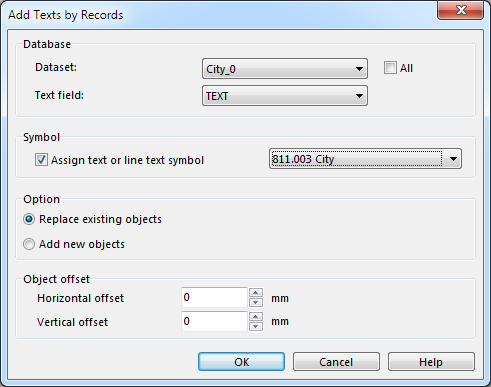
Click '''Add Texts by Records...''' in '''Database''' menu to create the text objects. The '''[[Database#Add_Texts_by_Records|Add Texts by Records]]''' dialog appears. | |||
[[File:ImportShapeText2.png]] | |||
Choose the option '''Replace existing objects''' and click '''OK''' to create the text objects. | |||
[[File:ImportShapeText3.png|600px]] | |||
[[File: | ==Import Shape Files in Orienteering Edition [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]]== | ||
This function needs [http://www.ocad.com/en/downloads/service-update OCAD 12.1.2 or higher]. | |||
Geodata are often provided in the Shape file format. Get some information about '''Shape Files''' on '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shape_file Wikipedia]'''. | |||
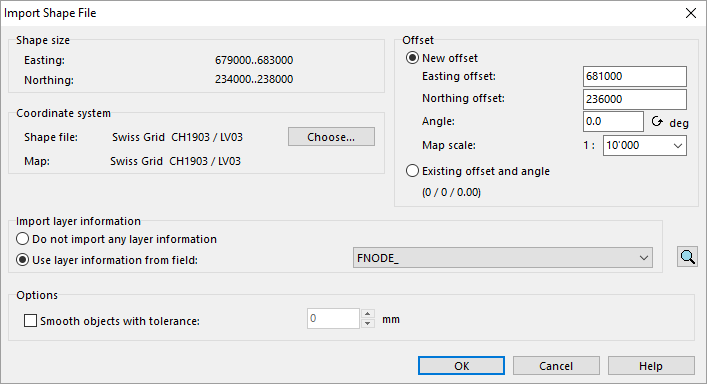
If you choose an '''ESRI Shape File''' in the '''Import''' dialog, the '''Import Shape File''' dialog appears. | |||
[[File:ImportShapeFileOrienteering.PNG|707px]] | |||
The import dialog offers the following options: | |||
'''Shape size:''' | |||
* This box shows the dimension of the data in the shape file using its coordinates. | |||
'''Coordinate System:''' | |||
* This box allows you to transform the imported Shape file data to the maps coordinate system. Click the '''Choose''' button to choose the Shape file's coordinate system if it is different to the map coordinate system. | |||
Choose a | '''Offset:''' | ||
* '''New offset:''' Choose this option when importing the first shape file to the actual map and if the map is not georeferenced yet. OCAD proposes reasonable easting and northing offset values. OCAD also proposes a map scale that the entire map in the shape file fits into the drawing area of OCAD. | |||
* '''Existing offset and angle:''' Select this option when importing the second and the following shape file to the actual map or if the map is already georeferenced. The new shape file will then fit to the already imported shape files. | |||
'''Import layer information:''' | |||
* '''Do not import any layer information:''' Select this option if no layer information should be imported. | |||
* '''Use layer information from field:''' Select this option if you want to import layer information (ex. lake, forest, street classes etc.) from a specified dBase field. This allows you to choose '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu to assign symbols to the imported data. | |||
* '''View table:''' Click on this [[File:ImportShapeFileOrienteeringViewTable.PNG]] button to see the dBase table. The '''[[Database#View_and_edit_table|View Table]]''' dialog opens. This table helps to decide which field contains the layer information. It is not possible to edit this table. | |||
Example: | |||
'''XYZ-File | [[File:ImportShapeFileOrienteeringDatabaseTable.PNG|777px]] | ||
This Shape file contains roads. In the database field ''OBJECTVAL'' is the road classification. So choose this field to import for each street object the classification. | |||
'''Smooth objects''' | |||
Additional option whether objects imported from shape file should be smoothed with a tolerance. | |||
==Import SOSI Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose this function import SOSI files. | |||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOSI SOSI] is a much used geospatial vector data format predominantly used for exchange of geographical information in Norway. | |||
The Norwegian Mapping Authority [http://kartverket.no Kartverket] released its map data in SOSI file format [http://www.statkart.no/Kart/Gratis-kartdata/Last-ned-gratis-kartdata/ for free use] in September 2013. | |||
This example shows the import of the N50 Kartdata, UTM 32 data of Oslo. Each community consists of 8 SOSI files. | |||
Choose '''Import''' from the '''File''' menu. Select all sos-files except the uft8 text file. Otherwise you will import every text label twice. | |||
[[File:SOSI_import.png|600px]] | |||
Click Open. The Import SOSI File dialog appears. | |||
[[File:SOSI_import_2.png]] | |||
OCAD has already two predefined crt tables for Orienteering maps which assigns the imported layers to symbols. Both crt files are in the OCAD program subfolder ''crt\''. | |||
* SOSI_2_ISSOM.crt: Convert the objects from SOSI layers to the symbols of sprint orienteering maps (ISSOM in the scale 1:4000 or 1:5000). | |||
* SOSI_N50_2_ISOM.crt: Convert the objects from SOSI layers to the symbols of orienteering maps (ISOM in the scale 1:10000 or 1:15000) | |||
Click '''Choose''' to choose another crt file or '''X''' if you do not want to use a crt file. | |||
Read more about crt-files in the [[Cross Reference Table]] article. | |||
Click OK to import the files. | |||
[[File:SOSI_import_3.png|800px]] | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] OCAD imports only vector objects. OCAD doesn't support the RASTER object. | |||
==Import SVG Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]]== | |||
[[http://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/ SVG]] stands for Scalable Vector Graphics, an XML-based file format for two-dimensional vector graphics. Choose an SVG file (*.svg) in the '''Import''' dialog and click the open button.<br> | |||
The objects from the SVG file are imported into OCAD as [[Image_Objects|image objects]]. The layer names are imported with the objects. The layer name is displayed in the left part of the status bar if an image object is selected. <br> | |||
[[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] Use '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbol]]''' from the '''[[Map]]''' menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects. | |||
==Import WMF Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose this function to import Windows Metafile. | |||
This import file format is obsolete. | |||
==Import CSV and XYZ Files [[File:Space.PNG]][[File:Pro40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Professional.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-cartography]][[File:Std40px.PNG|This function is available in OCAD Orienteering.|link=https://www.ocad.com/en/products/ocad-for-orienteering]]== | |||
Choose this function to import csv and xyz files. | |||
csv (Comma-separated values) files contain coordinates and other information like text label. Read more about [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comma-separated_values CSV] in [http://en.wikipedia.org/ Wikipedia]. | |||
xyz files contain 3d coordinate values. | |||
: [[File:Hint.jpg|hint]] Real world coordinates must be chosen in '''Scale and Coordinate System''' dialog from the '''Map''' menu and map offset must be set that the imported points are within the drawing area. | |||
[[File:CsvFileImportSymbol.png]] | |||
Specify the Northing, Easting and optionally the Height field. Specify the unit of measure and choose a point or text symbol that should be assigned to the imported objects. | |||
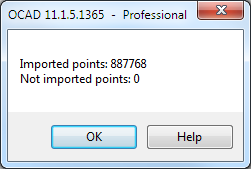
OCAD will create point and text objects with x/y coordinates. Height values are assigned to the objects' height property. Select an object and show '''Object Information''' to see height value of the selected object. | |||
After the import OCAD shows a summery about the imported points. | |||
[[File:XyzFileImportSummary.png]] | |||
=== CSV File Example with Comma as Separator === | |||
W13,457538.286,287921.422,105.426,A | |||
W14,457530.267,287906.700,105.351,A | |||
W15,457513.024,287892.899,105.736,B | |||
W16,457509.835,287889.936,105.788,D | |||
W17,457495.739,287896.681,106.758,C | |||
=== XYZ-File Example Space as Separator and File Header=== | |||
EASTING NORTHING HEIGHT | |||
579609.39 335648.46 701.00 | 579609.39 335648.46 701.00 | ||
579609.40 335627.71 698.79 | 579609.40 335627.71 698.79 | ||
| Line 150: | Line 314: | ||
579609.41 335674.01 704.39 | 579609.41 335674.01 704.39 | ||
=== Example === | |||
The following example shows the result of DTM xyz file import. | |||
[[File:XyzFileImport.png|300px]] | |||
OCAD created for each data point a point object which are assigned to a point symbol (black dot). | |||
[[ | ==Converting a Layer Manually== | ||
When importing a file which is not an OCAD file, '''[[Unsymbolized Objects]]''' are created. They appear in the color specified in '''[[OCAD_Preferences#Unsymbolized_objects|OCAD Preferences]]'''. | |||
[[File:ImportDxfUnsymbolized.png]] | |||
When you select such an object, a layer name will appear on the left side of the '''[[Graphical User Interface#Status Bar|Status Bar]]'''. To get a real map, the layers have to be converted to OCAD symbols. | |||
Normally you convert layers using the '''[[Map#Convert_Imported_Layers_to_Symbols|Convert Imported Layers to Symbols]]''' command from the '''Map''' menu. | |||
Normally you convert layers using the '''Convert Layers to | |||
You can also convert a layer manually: | You can also convert a layer manually: | ||
# Select | # Select an imported unsymbolized object. On the left side of the '''[[Graphical User Interface#Status Bar|Status Bar]]''' the layer name is shown. | ||
# Select the corresponding OCAD symbol in the symbol box. | # Select the corresponding OCAD symbol in the symbol box. | ||
# | # Choose the '''[[Change_Symbol|Change symbol for all objects with this symbol]]''' function in the '''Object''' menu or the [[File:Icon ChangeSymbolForAllObjectsWithThisSymbol.PNG]] button in the '''Edit Functions Toolbar'''. | ||
# Leave the preset values unchanged and click OK. | # Leave the preset values unchanged and click the '''OK''' button. | ||
---- | |||
Back to [[Main Page]] | |||
Previous Chapter: [[Background Map]] | Previous Chapter: [[Background Map]] | ||
Next Chapter: [[Drawing an Object]] | Next Chapter: [[Drawing an Object]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:39, 28 November 2017
Choose this command in the File menu to import an external file to the current map. The Import dialog box is displayed. Initially all importable files are listed. The following file types can be imported:
- OCAD map files (*.ocd)
- Adobe Illustrator files (*.ai) (only vector data)
- CSV files (*.csv)
- DXF files (*.dxf)
- Enhanced Meta files (*.emf) (only vector data)
- GML files (*.gml)
- GPX files (*.gpx)
- KML files (*.kml)
- OpenStreetMap files (*.osm)
- NMEA files (*.nmea)
- PDF files (*.pdf) (only vector data)
- Freehand XML files (*.rcw)
- Shape files (*.shp)
- SVG files (*.svg)
- Windows Meta files (*.wmf) (only vector data)
- xyz files (*.xyz)
![]() It is possible to select and import multiple dxf, gpx, nmea, shp and xyz files in this dialog box.
It is possible to select and import multiple dxf, gpx, nmea, shp and xyz files in this dialog box.
![]() OCAD opens the File Dialog in the folder of the last imported file. Press the Shift key to open a file from the Templates folder. The Templates folder is a subfolder of OCAD program folder (e.g. C:\Program Files\OCAD\OCAD 12 Mapping Solution\Templates).
OCAD opens the File Dialog in the folder of the last imported file. Press the Shift key to open a file from the Templates folder. The Templates folder is a subfolder of OCAD program folder (e.g. C:\Program Files\OCAD\OCAD 12 Mapping Solution\Templates).
Import OCAD Map 



Choose an OCAD-File (*.ocd) in the Import dialog box and click the open button. The Import OCAD Map dialog appears with the following options:
Position
- Place using the mouse: Choose this option to import for example a logo. The imported map is displayed in the center of the screen and all objects are selected. Thus, you can drag it with the mouse to the desired position.
- Place with offset: Choose this option when combining different parts of a map. Enter the offset in mm where the origin (0, 0) of the imported map should be placed.
- Use real world coordinates: Choose this option to import a georeferenced map. The map is automatically placed at the correct position.
![]() There will be a warning if the coordinate systems are different.
There will be a warning if the coordinate systems are different.
Symbols
- Do not import any symbols and colors: Choose this option to not import any symbols and colors.
- Import symbols only if symbol number does not exist yet: Choose this option to import symbols only if the symbol number does not exist yet. The symbol signature will not be compared. OCAD will not produce a new symbol if there is a symbol with an equal symbol number but a different signature. Colors will not be imported.
- Import symbols that do not exist. If the imported symbol number exists then a new symbol number is applied: Choose this option to import symbols if they do not exist. OCAD will produce a new symbol if there is a symbol with an equal number but a different signature. The new symbol number gets the next unused decimal (e.g. 102.001 becomes 102.002). Colors will not be imported. This option accords with the data import function of OCAD 8.
- Import all symbols and colors: Choose this option to import all symbols and colors from the imported map(for example to print 2 maps with different symbol sets and color tables). There are two options to import the Colors either at the top or at the bottom of the color table.
- Change symbol status from Normal to Protect: Check this option to change to symbol status off the imported symbols from Normal to Protect. This option is recommanded for importing an ocd map into a course setting project.
- Rotate objects with symbols orientated to north: This option is only available if the Real world coordinates options are turned on in the current and the imported map file and if the real world angle property is different in both maps. Select this option if the imported objects with north oriented symbols shall be rotated by this angle difference.
- Use CRT file: Activate this button to use a CRT converting table. This table consists of two columns, which are separated by a blank. In the first column there is the symbol number of the OCAD symbol in the map which is to be imported. In the second column there is the symbol number of the opened OCAD file. Visit the Cross Reference Table page to get more information about CRT-Files.
- Example:
526.0 813.1
- That means that all objects with the symbol number 526.000 will get the number 813.001 after the import.
- Load: Click this button to load a CRT file.
Database
- Database, Import existing database connections: This option is enabled if the import file contains database connections. When this option is choosen then OCAD creates a new database connection to the existing database if there is not already a database connection with the same name and file path in the OCAD file. Please note that OCAD creates a new connection with a new name if a dataset with the same name but another file path exists. Otherwise OCAD uses the existing dataset. OCAD does not merge databases.
![]() Please note that this CRT file is not compatible with the CRT files created in
Convert Layers dialog! A list of all CRT-Files which can be used with OCAD can be found on the Cross Reference Table page.
Please note that this CRT file is not compatible with the CRT files created in
Convert Layers dialog! A list of all CRT-Files which can be used with OCAD can be found on the Cross Reference Table page.
![]() The error message: "Cannot import symbol" appears if OCAD could not import a symbol. The import is aborted.
The error message: "Cannot import symbol" appears if OCAD could not import a symbol. The import is aborted.
Import Adobe Illustrator File 


Choose an Adobe Illustrator file (*.ai) in the Import dialog and click the open button. Files from Illustrator version 4 and later can be imported.
The objects from an Adobe Illustrator file are imported into OCAD as image objects. The layer names are imported with the objects. The layer name is displayed in the left part of the status bar if an image object is selected.
![]() Use Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects.
Use Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects.
Import DXF File 



DXF stands for Drawing Exchange Format and is a CAD data file format developed by Autodesk made for data exchange between AutoCAD and other programs (Read more in the Wikipedia Article).
Choose a DXF-File (*.dxf) in the Import dialog and click the open button.
The Import DXF-File dialog appears with the following options and information:
- DXF size: This box shows the range of the coordinates in the DXF file.
- Offset: Choose here whether you want to change the OCAD real world coordinates or to keep the existing ones.
- New offset: Choose this option if no real world coordinates are defined for the map. If you leave the proposed offset unchanged, the imported objects will be placed in the center of the OCAD drawing area. In addition, you can set the desired scale of the OCAD map here.
- Existing offset and angle: Choose this option if the map already has real world coordinates and you want to fit the imported DXF file to the existing coordinates.
- Coordinates: Define here how the coordinates of the DXF file should be interpreted. OCAD does not support WGS 84 coordinates.
- GIS (1 meter/unit): Choose this option when importing DXF files from Geographic Information Systems (GIS), where 1 unit in the DXF-File corresponds to 1 meter in the real world. The map scale is used for the transformation. Choose Scale and Coordinate System from the Map menu to set the map scale.
- GIS (1 millimeter/unit): Choose this option when importing DXF files from Geographic Information Systems (GIS), where 1 unit in the DXF-File corresponds to 1 millimeter in the real world. Usually GIS data uses the unit meter. Please check the unit of the dxf data before importing the data into OCAD.
This example is from British Ordnance Survey data. The dxf size and the proposed new offset is in millimeter.
- Other: Choose this option when importing DXF files from graphic programs. Enter the size in millimeters of one DXF unit on the map (e.g. if the DXF units are inches, enter 25.4).
- Convert text Objects from OEM to Unicode: Activate this box if the text in the DXF file is encoded in the OEM character set. OEM character set is used by old DOS programs and concerns only accented characters (ä, à, å etc.). Windows programs normally produce text in the ANSI character set. If accented characters are not imported correctly, try this option.
- Import INSERT as point object: Activate this option to import INSERT objects in the DXF file as point objects in OCAD. Otherwise the definition of INSERT objects is imported.
- CRT: Click this button if you have converted a similar DXF file before using Convert layers. A file dialog box appears. Choose the CRT file created with the Convert layers command. Read more about CRT-Files on the Cross Reference Table page. You will find examples there, too.
![]() If you do not use a CRT-File for importing a DXF-File, the DXF objects are imported as Unsymbolized Objects. Use the Convert Imported Layers to Symbol function in the Map menu to assign the objects to a symbol later on.
If you do not use a CRT-File for importing a DXF-File, the DXF objects are imported as Unsymbolized Objects. Use the Convert Imported Layers to Symbol function in the Map menu to assign the objects to a symbol later on.
Import EMF File 


Choose this function to import Windows Enhanced Metafile.
This import file format is obsolete.
Import GML Files

Choose this function to import Normbasierte Austauschschnittstelle (NAS) data.
OCAD cannot import other GML files.
Import GPX File 


Choose the .gpx file format in the Import File dialog. Read more about importing GPX files in the GPS - Import from File article.
This function is also available for the OCAD 12 Starter and the
OCAD 12 Course Setting Edition. For this purpose, choose the Import from File command in the GPS menu.
Import KML File 

Choose the *.kml format in the file import dialog to import Keyhole Markup Language (KML) files.
The line color, line width and fill color of the objects is also imported.
Import OSM Files 



A description of this function with an example can be found on the Import Open Street Map Files page.
Import NMEA Files 


Choose the .nmea file format in the Import File dialog. Read more about importing NMEA files in the GPS - Import from File article.
This function is also available for the OCAD 12 Starter Edition. For this purpose, choose the Import from File command in the GPS menu.
Import PDF Files 


Choose a PDF-File in the Import dialog and click the Open button. The Save Cross Reference Table dialog appears. If you want to save a CRT-File, click the Save button. If you want to continue without saving a CRT-File, click the Cancel button. Learn more about CRT-Files on the Cross Reference Table page.
The PDF-File is displayed in the middle of the current view of the map. All objects are selected, hence, it can be easily moved to the desired position.
Please note, that it is only possible to import vector PDF-Files. If the PDF-File contains raster images, they are displayed as a grey area on the map.
![]() Vector objects in PDF-Files are imported as Image Objects and can be converted to symbols using the Convert Imported Layers to Symbols function. Learn how to make a point symbol out of a vector graphic by reading the Create a Point Symbol out of Vector Data article.
Vector objects in PDF-Files are imported as Image Objects and can be converted to symbols using the Convert Imported Layers to Symbols function. Learn how to make a point symbol out of a vector graphic by reading the Create a Point Symbol out of Vector Data article.
Import Freehand XML Files 

Choose a Freehand XML File (*.rcw) in the Import dialog and click the open button. The Import Freehand XML dialog appears with the following options:
Font name translation:
- Select the load font name translation table option if the Macintosh font names used in the Freehand XML file should be translated to the Windows font names. This translation is defined in a cross reference table (*.crt).
- Example:
NicV-Normal;NicV
- That means the font of all objects that used the NicV-Normal in Freehand will be changed to NicV after the import.
- Load: Click this button to load a CRT file.
- File name: The file name of the loaded CRT file is shown here.
Geo-referenceing layer:
- Imported layer: OCAD offers a coarse georeferecing for Freehand XML files if the Freehand XML file contains a layer with coordinate values. This layer must be entered in the imported layer text box.
Convert imported layers to symbols:
- Select this option if the imported layers should be converted to OCAD symbols. This step can be done also after the import by using Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu.
Import Shape Files 

Get some information about Shape Files on Wikipedia.
If you choose an ESRI Shape File in the Import dialog, the Import Shape File dialog appears.
The import dialog offers the following options:
Shape size:
- This box shows the dimension of the data in the shape file using its coordinates.
Coordinate System:
- This box allows you to transform the imported Shape file data to the maps coordinate system. Click the Choose button to choose the Shape file's coordinate system if it is different to the map coordinate system.
Offset:
- New offset: Choose this option when importing the first shape file to the actual map and if the map is not georeferenced yet. OCAD proposes reasonable easting and northing offset values. OCAD also proposes a map scale that the entire map in the shape file fits into the drawing area of OCAD.
- Existing offset and angle: Select this option when importing the second and the following shape file to the actual map or if the map is already georeferenced. The new shape file will then fit to the already imported shape files.
New database type:
- When importing Shape files, OCAD creates a new database for each Shape file. You can choose between the database types dBase, Microsoft Access 2007 accdb and Microsoft Access 2003/2010 mdb.
- Microsoft Access databases are much faster than dBase and support Unicode. dBase is more compatible with Shape export.
- If one of the Microsoft Access options is chosen then the code page of the imported Shape file's dBase file should be declared. This is important to ensure a correct text conversion from dBase (Ansi) to Microsoft Access (Unicode) conversion.
- Choose Do not create a database when you do not need the attribute data. Then OCAD imports only the geometry from the Shape file. You can add one attribute as layer name when choosing the option Use layer information from field.
Key field in database: OCAD creates a copy of the Shape file's dBase file during the import process. OCAD can optionally add an additional key field to the copied dBase file.
- Create new key field: Select this option, if the dBase file does not contain a key field with a unique key for each object or if you are not sure if such a key field exists.
- Use existing key field: Select this option, if the dBase file already contains a key field and you are sure that it contains a unique key for each object. Select the key field.
- View table: Click on this button to see the dBase table. The View Table dialog opens. This table helps to decide which key field can be used. It is not possible to edit this table.
Import layer information:
- Do not import any layer information: Select this option if no layer information should be imported. Symbols must be assigned with Assign Symbols by Records command in Database menu. This may takes a lot of time.
- Use layer information from field: Select this option if you want to import layer information (ex. lake, forest etc.) from a specified dBase field. This allows you to choose Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to assign symbols to the imported data.
- View table: Click on this button to see the dBase table. The View Table dialog opens. This table helps to decide which field contains the layer information. It is not possible to edit this table.
![]() Check the Field 2 box to choose a 2nd database field. In that case the imported layer information will be both field values, concatenated by an underscore: FieldValue1_FieldValue2.
Check the Field 2 box to choose a 2nd database field. In that case the imported layer information will be both field values, concatenated by an underscore: FieldValue1_FieldValue2.
Smooth objects
Additional option whether objects imported from shape file should be smoothed with a tolerance.
Import Text or Line Text Objects
There are no text objects in Shape files. The texts like city names or river names are stored as attributes of the objects in the Shape file's dBase file. You can create text objects from imported point objects or line text objects from imported line objects by using Add Texts by Records... in the Database menu.
Example
After importing the Shape file the objects appear in OCAD as unsymbolized objects. The label of the selected object is stored in the according database record ('Baar' in the field 'TEXT').
Click Add Texts by Records... in Database menu to create the text objects. The Add Texts by Records dialog appears.
Choose the option Replace existing objects and click OK to create the text objects.
Import Shape Files in Orienteering Edition 

This function needs OCAD 12.1.2 or higher.
Geodata are often provided in the Shape file format. Get some information about Shape Files on Wikipedia.
If you choose an ESRI Shape File in the Import dialog, the Import Shape File dialog appears.
The import dialog offers the following options:
Shape size:
- This box shows the dimension of the data in the shape file using its coordinates.
Coordinate System:
- This box allows you to transform the imported Shape file data to the maps coordinate system. Click the Choose button to choose the Shape file's coordinate system if it is different to the map coordinate system.
Offset:
- New offset: Choose this option when importing the first shape file to the actual map and if the map is not georeferenced yet. OCAD proposes reasonable easting and northing offset values. OCAD also proposes a map scale that the entire map in the shape file fits into the drawing area of OCAD.
- Existing offset and angle: Select this option when importing the second and the following shape file to the actual map or if the map is already georeferenced. The new shape file will then fit to the already imported shape files.
Import layer information:
- Do not import any layer information: Select this option if no layer information should be imported.
- Use layer information from field: Select this option if you want to import layer information (ex. lake, forest, street classes etc.) from a specified dBase field. This allows you to choose Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to assign symbols to the imported data.
- View table: Click on this
button to see the dBase table. The View Table dialog opens. This table helps to decide which field contains the layer information. It is not possible to edit this table.
Example:
This Shape file contains roads. In the database field OBJECTVAL is the road classification. So choose this field to import for each street object the classification.
Smooth objects Additional option whether objects imported from shape file should be smoothed with a tolerance.
Import SOSI Files 


Choose this function import SOSI files. SOSI is a much used geospatial vector data format predominantly used for exchange of geographical information in Norway.
The Norwegian Mapping Authority Kartverket released its map data in SOSI file format for free use in September 2013.
This example shows the import of the N50 Kartdata, UTM 32 data of Oslo. Each community consists of 8 SOSI files.
Choose Import from the File menu. Select all sos-files except the uft8 text file. Otherwise you will import every text label twice.
Click Open. The Import SOSI File dialog appears.
OCAD has already two predefined crt tables for Orienteering maps which assigns the imported layers to symbols. Both crt files are in the OCAD program subfolder crt\.
- SOSI_2_ISSOM.crt: Convert the objects from SOSI layers to the symbols of sprint orienteering maps (ISSOM in the scale 1:4000 or 1:5000).
- SOSI_N50_2_ISOM.crt: Convert the objects from SOSI layers to the symbols of orienteering maps (ISOM in the scale 1:10000 or 1:15000)
Click Choose to choose another crt file or X if you do not want to use a crt file.
Read more about crt-files in the Cross Reference Table article.
Click OK to import the files.
![]() OCAD imports only vector objects. OCAD doesn't support the RASTER object.
OCAD imports only vector objects. OCAD doesn't support the RASTER object.
Import SVG Files 

[SVG] stands for Scalable Vector Graphics, an XML-based file format for two-dimensional vector graphics. Choose an SVG file (*.svg) in the Import dialog and click the open button.
The objects from the SVG file are imported into OCAD as image objects. The layer names are imported with the objects. The layer name is displayed in the left part of the status bar if an image object is selected.
![]() Use Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects.
Use Convert Imported Layers to Symbol from the Map menu to convert the imported objects from image objects to symbolized OCAD objects.
Import WMF Files 


Choose this function to import Windows Metafile.
This import file format is obsolete.
Import CSV and XYZ Files 


Choose this function to import csv and xyz files.
csv (Comma-separated values) files contain coordinates and other information like text label. Read more about CSV in Wikipedia.
xyz files contain 3d coordinate values.
 Real world coordinates must be chosen in Scale and Coordinate System dialog from the Map menu and map offset must be set that the imported points are within the drawing area.
Real world coordinates must be chosen in Scale and Coordinate System dialog from the Map menu and map offset must be set that the imported points are within the drawing area.
Specify the Northing, Easting and optionally the Height field. Specify the unit of measure and choose a point or text symbol that should be assigned to the imported objects. OCAD will create point and text objects with x/y coordinates. Height values are assigned to the objects' height property. Select an object and show Object Information to see height value of the selected object.
After the import OCAD shows a summery about the imported points.
CSV File Example with Comma as Separator
W13,457538.286,287921.422,105.426,A W14,457530.267,287906.700,105.351,A W15,457513.024,287892.899,105.736,B W16,457509.835,287889.936,105.788,D W17,457495.739,287896.681,106.758,C
XYZ-File Example Space as Separator and File Header
EASTING NORTHING HEIGHT 579609.39 335648.46 701.00 579609.40 335627.71 698.79 579609.40 335659.36 702.60 579609.40 335729.36 711.52 579609.40 335766.15 715.91 579609.41 335674.01 704.39
Example
The following example shows the result of DTM xyz file import.
OCAD created for each data point a point object which are assigned to a point symbol (black dot).
Converting a Layer Manually
When importing a file which is not an OCAD file, Unsymbolized Objects are created. They appear in the color specified in OCAD Preferences.
When you select such an object, a layer name will appear on the left side of the Status Bar. To get a real map, the layers have to be converted to OCAD symbols.
Normally you convert layers using the Convert Imported Layers to Symbols command from the Map menu. You can also convert a layer manually:
- Select an imported unsymbolized object. On the left side of the Status Bar the layer name is shown.
- Select the corresponding OCAD symbol in the symbol box.
- Choose the Change symbol for all objects with this symbol function in the Object menu or the
button in the Edit Functions Toolbar.
- Leave the preset values unchanged and click the OK button.
Back to Main Page
Previous Chapter: Background Map
Next Chapter: Drawing an Object